To fully understand digital transformation, it helps to look at examples of this emerging tech trend. Examples can inspire businesses considering investment in this rising trend by offering tangible instances of the benefits of digital transformation.
Digital transformation is the process of replacing or enhancing traditional business processes with digital technologies. The goal is to improve and streamline processes at all levels. In a now common example, many medical offices are paper-free, or are moving that way. Patients fill out medical documents on a tablet and records are migrated through the system digitally, replacing the highly inefficient paper folders from yesteryear.
Even with a relatively modest example like shifting from paper to electronic records, digital transformation can dramatically improve how companies serve their customers. However, as you’ll see in the examples below, digital transformation can require a seismic shift in process, which means considerable investment of time and money in technology and staffing.
Virtually every example of digital transformation requires some form of cloud computing, and often uses more than one cloud provider. Certainly most examples require machine learning, a significant element of data analytics, and – increasingly – support from artificial intelligence software.
Needless to say, most businesses can’t achieve this transformation on their own; they’ll need to partner with digital transformation companies to enhance their odds of success. But because the advantages are so great, even deep investment is typically justified. In the long run, many digital transformation deployments become examples of success.
Also see: Top 10 Digital Transformation Companies
Examples of Digital Transformation
Digital Transformation in Retail
In 2017, Domino’s Pizza adopted artificial intelligence and chatbot technology to create a conversational interface with Facebook Messenger. Customers who have a Domino’s Pizza account can use Facebook Messenger to quickly reorder a previously ordered pizza combination or a new series of toppings.
Ordering is streamlined and interactive, and since it’s tied into social media (as opposed to requiring a separate web site or a phone call), the frequency of orders have increased. The chatbot uses a data-based logic system to offer upsells like strategic discounts and related food items. Additionally, the AI-based system saves labor costs for the pizza chain.
This example of digital transformation reflects the strength of AI in driving sales. One of AI’s main strengths is human-like chat, in which an algorithm responds to customers in real time using NLP (natural language processing), even if the customer is using idiosyncratic language. Additionally, AI excels at performing tedious tasks that would stretch the limits of human performance. This includes sifting through vast amounts of data to search for useful patterns and other insights – in this case, patterns in how humans order food delivery, to ease friction in the ordering process.
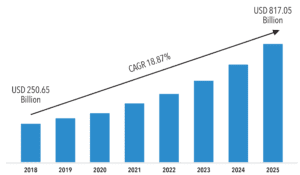
Given the many successful examples, it’s no surprise that the market for digital transformation services is forecast to top $800 billion by 2025. Source: MarketResearchFuture.
Digital Transformation in Marketing
In 2012, toy and game manufacturer Hasbro saw its marketshare slipping and had an epiphany. Rather than market to children, it targeted their parents, who actually make the purchases. They began a new digital and data strategy, which took a number of years to reach full implementation.
The company began gathering and mining customer data to create more targeted marketing campaigns, promoting both nostalgic and newer brands. It made a major push into online media, targeting web sites with high cohorts of parents. This data-based online approach gave Hasbro better and more immediate feedback. In 2016 the company broke the $5 billion sales mark for the year and is on track for $6 billion in 2021.
One of the main tools for digital transformation in marketing is data. Mining electronic data gathered in massive quantities in data warehouses and data lakes greatly increases the ability of sales leaders to hone campaigns. This usually involves business intelligence software – a core tool in digital transformation – which allows pinpoint targeting by demographics.
Digital Transformation in Banking
Institutions across the financial sector, such as Wells Fargo and Bank of America, have automated transactions, even as this has required handling major security and compliance issues. The fascinating aspect of this example is that instead of one limited instance, retail banks have undergone a rolling adoption of digital transformation over the last three decades.
The major milestone in this process was the adoption of Automated Teller Machines (ATMs); by allowing customers to get cash without human assistance, the banking sector has been a leader in using automation to save on staff costs. For a contrasting example, look at the grocery sector, which didn’t move heavily to self-checkout (SCO) until the last few years; globally, less than 200,000 units existed in 2013, a figure forecast to rise to 1.2 million units in 2025.
The banking sector is also a leader in digital transformation in its use of mobile. Its adoption of mobile banking uses a combination of edge computing (its network of security gateways) and IoT devices (cell phones) to provide convenience to customers. Going a step further, allowing customers to create automatic payments means that – at a very basic level – users are deploying automation themselves. Furthermore, third party payment systems like Google Pay and Apple Pay let consumers pay for everyday purchases with a wave of their smartphones; this is yet another example of deploying technology, Near Field Communication, to enable an easier process.
Digital Transformation in Transportation
There is a good reason Uber grabbed so much marketshare from traditional taxi companies over the last decade. Uber took an in-depth, data-driven look at the taxi industry and identified all the pain points of customers, from locating a nearby taxi to offering non-cash payments. Using a key element of digital transformation strategy – active listening using data – the company catered to customers in ways they’d never been responded to before.
All of this logistics and data-centered strategy was built into the smartphone app, which facilitates convenient and rapid customer feedback. Again, this is close listening to the customer.
This example of real time, interactive listening is echoed in a foundational practice in digital transformation: using social media to form a close bond with customers. The interactive smartphone app is a click away from major social media platforms and, in the minds of many consumers, is the same world. Clearly, social media has become the new customer service desk. LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook have replaced 800 lines and email for instant communication between sellers and customers, handling sales, disputes, and measuring brand sentiment.
In its “State of the Connected Customer” report, Salesforce found 84% of high-performing companies are managing and responding to social inquiries and issues in real time, while just 37% of under-performers say the same. As an additional advantage, this interactive response is often accompanied by a marketing element.
Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Telehealth services like Teladoc, MeMD, MDLive and a host of other providers enable users to receive care from healthcare professionals using a Webcam, lessening the need for physical infrastructure, including fewer staff hours spent supporting waiting rooms.
An advantage of digital transformation is better focus on the customer, and that’s certainly true with telehealth, which allows better care for rural and other isolated patients. Not to mention enabling an on-demand format that’s more flexible for all patients. The telehealth market is forecast to expand from $144 billion in 2020 to $636 billion by 2028.
Additionally, the healthcare sector is migrating to electronic data management at all levels, from patient sign-in on electronic devices to record keeping with blockchain and data warehouses. This helps create a centralized data repository for each patient known as an EHR, or electronic health record, which facilitates better care by pooling data from disparate sources.
Data management and data mining are rapidly growing trends in healthcare, easily rivaling telehealth as examples of digital transformation. Using data analytics on large number of anonymized patient records enables lower rates of medication problems by flagging consistent problems across many patients. Data is also used for preventative care, which involves analyzing patient data to find links between current and potential future medical problems, then informing the patient far in advance.